We all know what is the Reserve Bank of India(RBI). we see it in every currency note we use. we hear a lot of news regarding the RBI. we know it is the central bank of India, but there are more things we have to understand about RBI. In this post, we will discuss the RBI and its importance.
RBI-Reserve Bank of India

Reserve Bank of India is India’s central bank that commenced its operations on 1st April 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act 1934. and RBI was nationalized on 1st January 1949. and it is fully owned and regulated by the Government of India. RBI also is known as Banker’s bank and government’s banker. The concept behind the RBI was based on the strategies formulated by Dr. B.R Ambedkar on his book “The Problem of the Rupee-Its origin and its solution”. The RBI controls the monetary policy concerning the national currency, the Indian rupee. Following is the timeline of important events of the RBI.
| Year | Event |
| 1934 | The British made proposal for the Reserve Bank of India Act |
| 1935 | On April-1, The Reserve Bank of India was established in Calcutta |
| 1937 | Reserve Bank of India was permanently shifted to Mumbai |
| 1949 | RBI got nationalized after Independence |
Objectives of the RBI
- Manage the monetary system and the credit system in the country.
- To stabilize the internal and external value of the currency-Rupee.
- To maintain a balance between supply and demand of the currency.
- For a systematic and balanced development of banking in the country.
- Proper arrangement of agricultural finance.
- For the development of an organized money market in the country.
- For the proper arrangement of Industrial finance.
- proper management of public debts.
- To establish a monetary relationship with other countries in the world and international financial institutions.
- Centralization of cash reserves of commercial banks.
Functions of the RBI
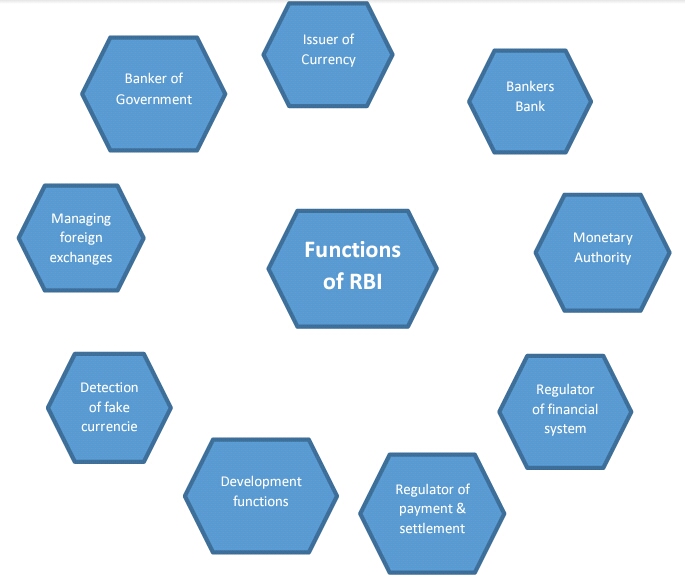
- The RBI is providing the public sufficient supply of currency notes and coins. and make the circulation stable.
- The quality of currency notes and coins are monitoring by the RBI also the FAKE notes detection and prevention.
- Removal of currency and coins that are not fit for circulating.
- Implementation of monetary policies.
- Monitoring the monetary policies.
- RBI is Ensuring price stability in the country.
- The RBI will determine the comprehensive parameters of banking operations in the country.
- RBI manages the FOREX Reserve of India.
- The RBI is maintaining the value of the Rupee outside the country, also It aids foreign trade payment.
- RBI Provides banking solutions to both central and state governments and also functions as their banker.
- RBI is the chief banker to all banks in the country and it maintains banking accounts of all scheduled banks.
Legal Framework
The RBI is bounded by the following Acts.
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934
- Public Debt Act, 1944
- Government Securities Regulations, 2007
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- Reconstruction and Securitization of Financial Assets, and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002
- Credit Information Companies(Regulation) Act, 2005
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007
Organization Structure
Operations of the Reserve Bank are monitored and governed by a central board of directors. RBI is on the whole operated with a 21-member central board of directors appointed by the Government of India with respect to the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- Reserve Bank of India is monitored and controlled by a central board of directors. The directors are appointed for a 4-year term by the Government of India under the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The Central Board consists of:
- Governor
- 4 Deputy Governors
- 2 Finance Ministry representatives
- 4 directors will represent the local boards headquartering at New Delhi,Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The executive head of RBI is Governor.
- The Governor is accompanied by 4 deputy governors.

Departments in RBI
- Issue Currency and its Management
- Banking Operations and Development
- Rural Planning and Employment Development Programs
- Developing and Maintaining Foreign Exchange Market in the Country (FEMA 1999)
Subsidiaries of Reserve Bank of India
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited (BRBNMPL)
- National Housing Bank (NHB)
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
RBI Offices
At present RBI is having 4 zonal offices, 19 regional offices, 11 sub-offices ,also two training collage for its officers.
Zonal offices
- North- New Delhi
- South- Chennai
- East- Kolkata
- West- Mumbai
Regional offices
RBI is having 19 regional offices at present.
- Thiruvananthapuram
- Patna
- Nagpur
- Lucknow
- Mumbai
- Kochi
- Kolkata
- Jammu
- Kanpur
- Chennai
- Delhi
- Guwahati
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhopal
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chandigarh
- Jaipur
- Bangalore
Sub-offices
RBI is having 11 sub-offices at present
- Agartala
- Aizawl
- Shillong
- Dehradun
- Gangtok
- Imphal
- Panaji
- Srinagar
- Raipur
- Shimla
- Ranchi
Training colleges
Currently, RBI has two training colleges for training their employees
- Reserve Bank of India Staff College- Chennai
- College of Agricultural Banking- Pune
Final Thoughts
As we all know Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of India. The RBI is playing a big role in the country’s economy and it control and monitors the entire banking and financial system. as a finance enthusiast, we must know basic details about the RBI. in this post we discussed RBI and its functions and importance. i hope this post will help you to understand the basics of the RBI

Pingback: The RBI Governor- a complete list of the RBI Governors - finvestfox.com